Unveiling the Hidden Gem: West Virginia’s Botanical Wonderland
Understanding West Virginia’s Planting Zones
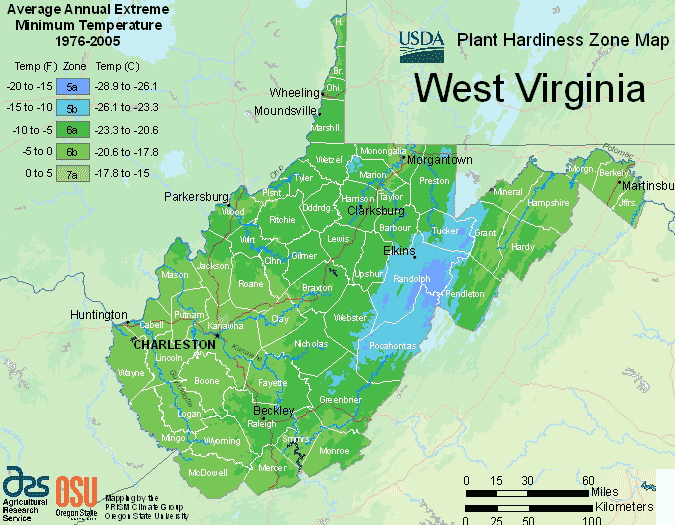
When it comes to , it’s crucial to know the specific climate conditions that affect the successful growth of plants in the state. West Virginia falls within USDA Hardiness Zones 5a to 7b, which means it experiences a range of temperatures and conditions that impact plant survival and growth. These zones help gardeners determine the best plants for their region based on average winter low temperatures.
In Zone 5a, which covers the northernmost part of West Virginia, temperatures can drop as low as -20°F (-28.9°C). Some suitable plants for this zone include tulips, daylilies, and hostas. Moving south into Zone 7b, where the climate is milder, plants such as roses, Japanese maples, and butterfly bushes thrive. West Virginia’s diverse topography and varying microclimates within the state also affect planting conditions, making it essential to consider factors like elevation, soil type, and sun exposure for successful gardening.
| Zone Features | Tips for Planting Success |
|---|---|
|
|

Choosing the Best Plants for Your West Virginia Garden
When it comes to creating a beautiful and thriving garden in West Virginia, knowing the correct planting zone is key. West Virginia falls primarily within USDA Hardiness Zones 5 and 6, which means it experiences cold winters and mild summers. This information is crucial in selecting plants that can withstand the region’s climate and thrive in your garden.
Consider incorporating a diverse range of plants that are well-suited to West Virginia’s planting zone. Some excellent choices for this region include native perennials like the vibrant Cardinal Flower (Lobelia cardinalis), the delicate Wild Blue Phlox (Phlox divaricata), and the showy Butterfly Weed (Asclepias tuberosa). These plants not only add a touch of natural beauty to your garden but also provide for local wildlife such as birds, bees, and butterflies. Additionally, don’t forget to include a variety of shrubs and trees like the aromatic Spicebush (Lindera benzoin) and the iconic Sugar Maple (Acer saccharum), which offer shade and height to your landscape. By carefully selecting plants that are well-suited to West Virginia’s planting zone, you can create a beautiful and sustainable garden that flourishes throughout the seasons.
| Features | Tips |
| Consider native perennials | Promote local wildlife and add natural beauty |
| Include a variety of shrubs and trees | Add shade and height to your landscape |
| Research specific plant requirements | Ensure optimal growing conditions for your chosen plants |

Factors to Consider When Planting in West Virginia
<p>When it comes to gardening and plant cultivation in West Virginia, being aware of the specific zone for planting is crucial. West Virginia spans USDA Hardiness Zones 5a to 7a, which indicates the type of plants that thrive best in the region's climate. Understanding the zone helps you select plants that are well-suited to the temperature and weather patterns prevalent in the state.</p>
<p>Aside from considering the zone, several other factors can greatly impact successful planting in West Virginia. The unique topography and varied microclimates within the state present an exciting opportunity for gardeners. However, it is vital to be mindful of these factors:</p>
<table style="width: 100%;">
<tr>
<td>Choose Cold-Hardy Plants</td>
<td>Consider selecting plants that can withstand occasional frost or harsh winter conditions, as temperatures can fluctuate drastically in West Virginia.</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Soil Composition</td>
<td>Understanding the soil type can greatly influence the health and growth of your plants. Conducting a soil test can provide insight into its pH level and nutrient content.</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Drainage Considerations</td>
<td>Ensure your chosen planting location has proper drainage to prevent waterlogging, as excess moisture can harm plants and impede their growth.</td>
</tr>
</table>
<p>Additionally, considering factors like sunlight exposure, plant hardiness, and the availability of water resources are essential in creating a thriving garden in West Virginia. By following these tips and understanding the unique characteristics of the region, you can create a garden that flourishes and brings joy throughout the seasons.</p><br/><img class="kimage_class" src="https://up-gardening.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/photo-1619974577285-9eb120fcf882.jpg" alt="Planting Tips for West Virginia Gardeners"><br/><h2 id="planting-tips-for-west-virginia-gardeners">Planting Tips for West Virginia Gardeners</h2><div>What Zone is West Virginia for Planting?
As gardening enthusiasts in West Virginia, understanding what planting zone you fall under is essential to ensure successful cultivation. West Virginia is situated in planting zones 5 and 6, which means the state experiences cold winters with average minimum temperatures ranging from -10°F (-23°C) to 0°F (-18°C). These zones are ideal for a variety of plants that can withstand lower temperatures, allowing gardeners to explore a diverse range of options.
When planning your garden in West Virginia, consider the following features and tips to help you create a flourishing outdoor oasis:
| Feature/Tips | Description |
|---|---|
| Choose cold-hardy plants | Opt for plants that can thrive in temperatures experienced during West Virginia winters. Examples include conifers, hellebores, and winterberry holly. |
| Plant frost-resistant vegetables | Focus on vegetables that can withstand light frosts, such as kale, spinach, and broccoli. These crops can often be planted as early as April or May. |
| Pay attention to soil drainage | West Virginia experiences a variety of soil types, so test your soil’s drainage capabilities and amend it accordingly. Proper drainage is crucial for plant health. |